Contents
What is Transistor?
A transistors a semi-conductor device corresponding to a thermionic vacuum triode. It is used in electronic circuit which is used as an oscillator or an amplifier.
It is short shaped, long durable and having no cathode heat energy. It is made of small pieces of semi-conductor substances like germanium or Silicon, with which at least three electric contacts are connected.
Generally, two rectifying contacts and one ohmic or non-rectifying contact are made which convert sound waves and we listen the sound.
Transistors operate at much lower power and are better than electronic tubes in many aspects. These are widely used in portable radios and television receivers.
Transistor was invented by John Bardeen and Walter House Brattain in 1948 and improved form was devised by William Bradford.
Types of Transistor
There are two types of transistor. They are —
- Point Contact Transistor &
- Junction Transistor.
Junction Transistor : There are two types of Junction transistor —
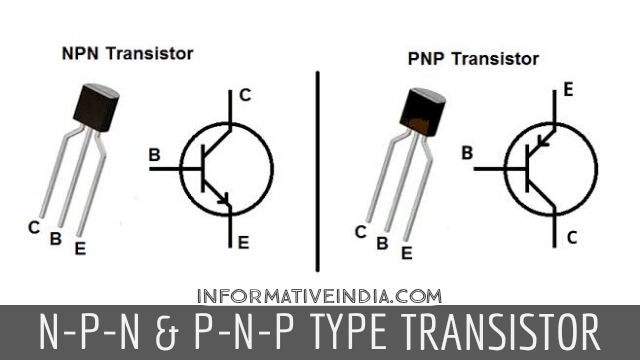
- P-N-P types &
- N-P-N types.
Working of P-N-P Transistor
To study the working of P-N-P type transistor, the emitter base circuit is forward biased with small voltage Veb, while collector base circuit is reverse biased with a voltage Veb.
The emitter base circuit being forward biased helps, the movement of the holes is P-type and electrons in N-type towards the junction between the emitter and base.
On the other hand, The collector base junction being reversed biased does not allow the holes in P-type and electrons in N-type to give towards the collector base junction.
The hole in the emitter and the electrons in the base are repealed by the positive and the negative terminals respectively of the battery Veb.
On reaching the emitter base junction a small fraction about 5% of the total number of holes combine with the electrons in the base to get neutralized.
As the base region is very thin and the collector is given a high negative potential the holes will rush towards the collector and about 95% of them are thus collected by it.
For each hole reaching the collector, an electron is released from the negative of the collector base battery Veb and neutralizes the hole. Also for each hole which is lost in the collector region a covalent bond near the-emitter breaks down and an electron is liberated which enters the positive terminal of the emitter-base battery.
Thus we see that the current is carried by the holes inside the crystal and by electrons in the external circuit.
In the emitter base external circuit the flow of electrons is from P to N and therefore, the Conventional current flows from N to P or base to emitter.
Similarly, In the collector base circuit the flow of electrons is from N to Pin the external circuit and hence a current Ic flows in the collector base circuit from P to N. The difference between le and Ic is the base current lb which flows in the direction of le.
Working of N-P-N transistor
In this case also the emitter base junction is forward biased while the collector-base circuit is reverse biased.
The holes in the base being repealed by positive terminal of the forward bias and the electrons in the emitter being repealed by the negative terminal move towards the emitter base junction.
On reaching the junction a small fraction of about 5% of total number of electrons combine with the holes at the base to get neutralized.
As the base layer is very thin and the collector is given a very high positive potential. The electrons will rush towards collector and about 95% of them are collected by it.
These electrons collected by the collector flow towards the positive of battery Veb. The deficiency of the electrons in the emitter is made up by the negative of the emitter base battery Veb.
Thus, the current is carried by the electrons both inside the crystal as well as in the external circuit. In the emitter base external circuit the flow of electrons is from P to N.
Hence the Conventional current le is from N to P. In the collector base circuit the flow of electrons in the external circuit is from N to P resulting in the current Ic from P to N.
You May Like —




